What is Hard Water?
All your questions answered...
Curious about what hard water actually is, why so many water companies are talking about it, and what problems it can cause? Below are a few ways that hard water can impact your life:
💧 Limescale
💧 Dry skin and hair
💧 Expensive bills
💧 A shorter lifespan on your appliances
The creation of hard water…

What is hard water?
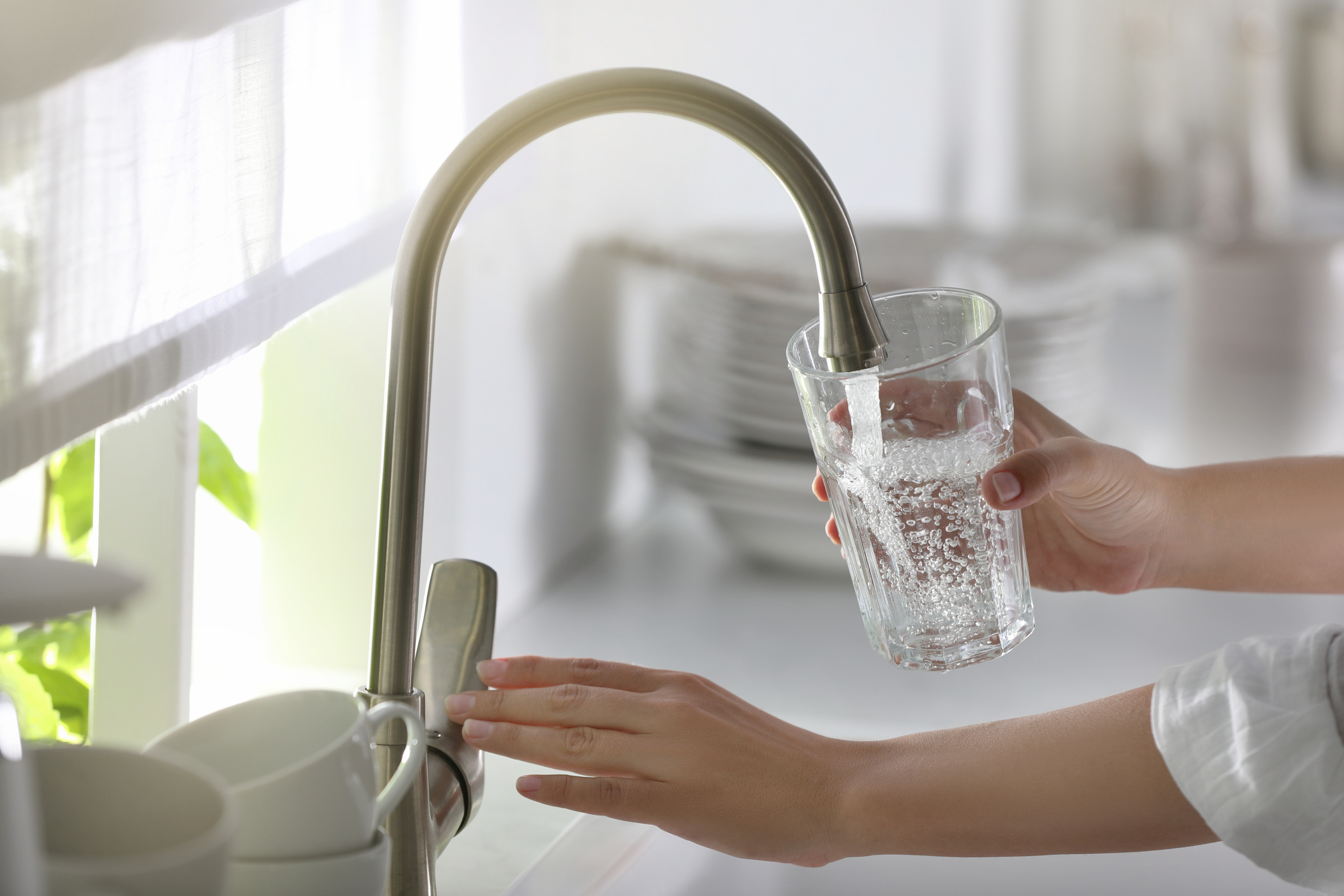
Hard water, containing minerals like magnesium and calcium, can cause problems for home pipes, attendances, and also for people skin and hair. Water starts soft but picks up minerals as it moves through the ground, making it hard. Places like the South East of England and London often have high water hardness. However, areas like Scotland, Ireland, and Wales usually have naturally soft water.
Water hardness measurement of your area is the first foundamental step to identify the levels of hard water and identify possibile correlations with issues are happening in your home.
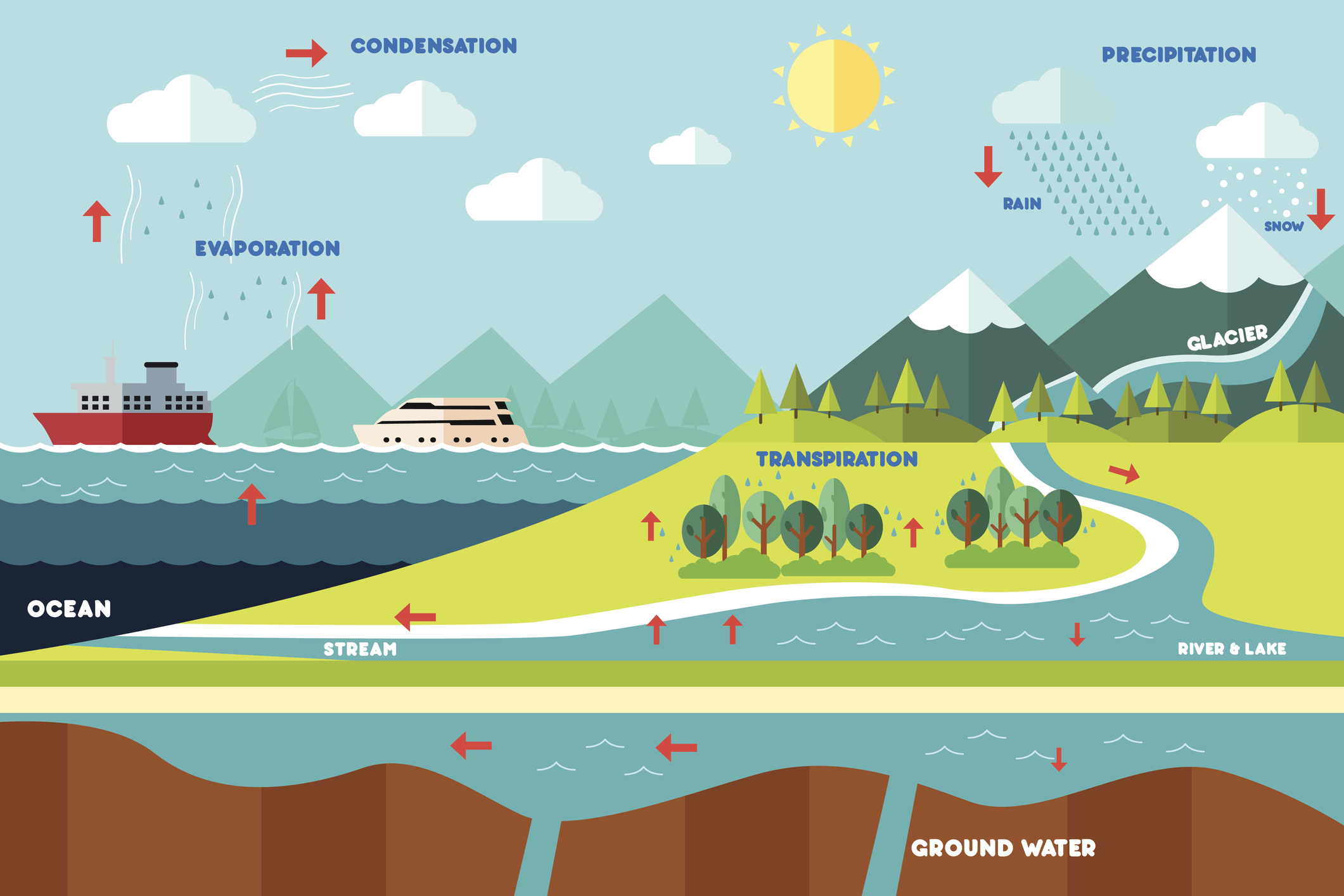
The Water Cycle
The sun heats water, making it evaporate into vapor, which rises into the air. As it cools, it forms clouds and eventually falls as rain. This water collects on the ground, replenishing rivers, lakes, and oceans, where it gets heated by the sun again, starting the cycle over. Only pure water forms clouds, resulting in mineral-free and soft rain. However, when water hits the ground, it starts to pick up hard minerals, which stay as it moves through reservoirs and into homes.
Hard water can lead to…
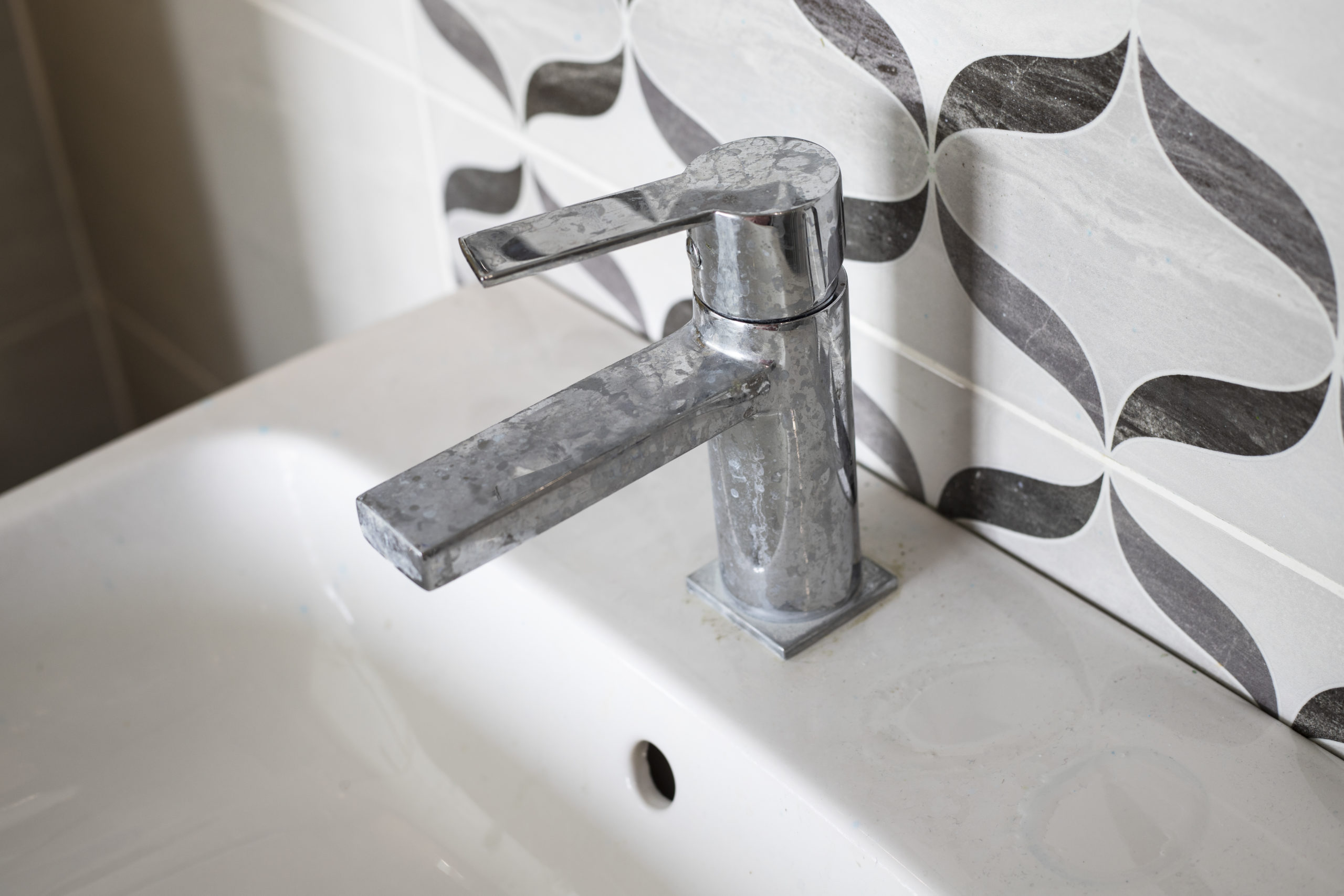

Limescale in your home
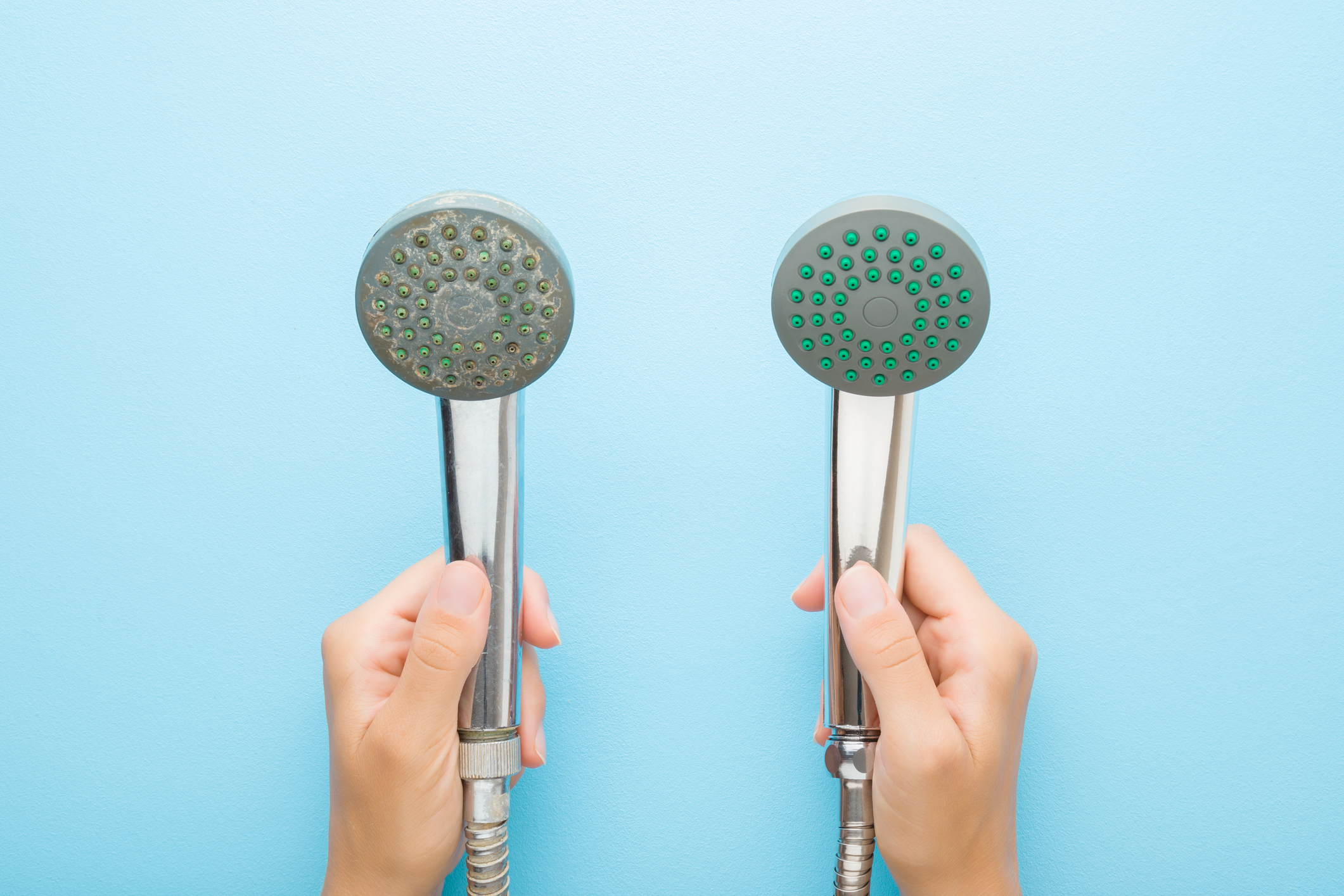
Hard water can lead to limescale buildup, which is tough for homeowners to deal with. Removing the limescale can be hard work. Also, limescale can make homes look dirty and less modern, which homeowners don’t like. Limescale can clog shower heads, damage appliance parts, and make them work less well and for a shorter time.
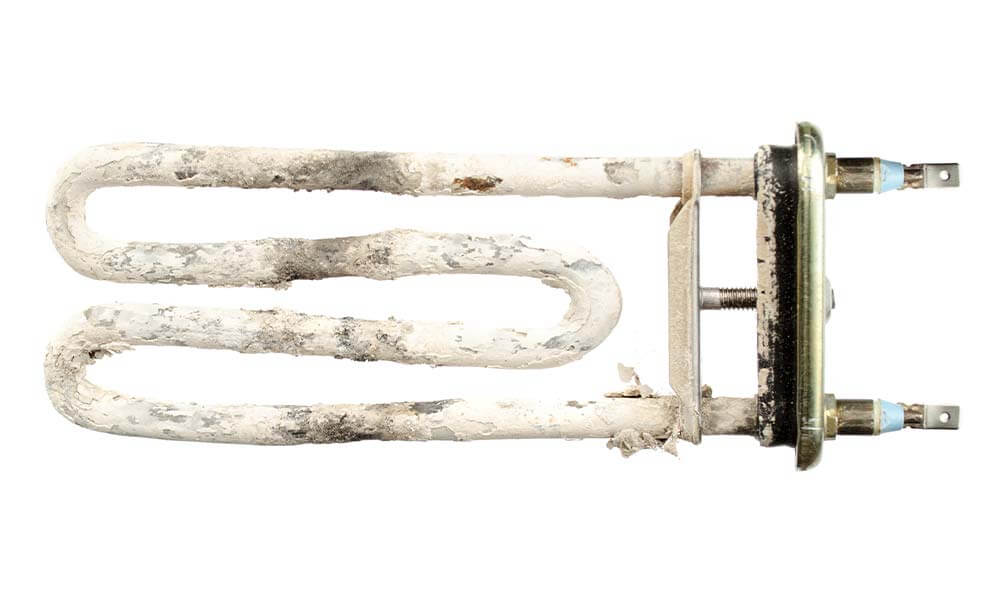

The effects of hard water
Hard water causes problems like scale and scum, seen as white marks around baths and sinks, often with leftover stuff on sinks, toilets, and showerheads. In bad cases, limescale can block pipes and make water heaters and other appliances stop working well. Also, hard water doesn’t mix well with soap, so it doesn’t clean as well. Clothes might look dull after washing, and dishes and glasses can look smeared.
Hard water can also affect hair, making it look dull and hard to deal with.

Your hair can also be affected by hard water, leaving it dull and difficult to manage. Find out more about hard water hair and how to treat it, here.
In our research, the main problems from hard water were damage to kitchen appliances (66%), plumbing (59%), boilers (58%), blocked pipes (48%), and heating systems that don’t work well (46%). Fewer people reported problems like undrinkable water (34%) and skin irritations (32%).
You can find out more about the benefits of softened water, here.

The benefits of soft water
1) Save money
Limescale from hard water can damage plumbing and appliances, leading to expensive repairs.
2) Save time
Say goodbye to scrubbing limescale from your drains, shower screens, tiles, and taps when you get a Harvey Water Softener.
An Harvey water softener system in your home could be a solution to prevent and remove the minerals that increase the effects of water hardness.

3) Feel the luxury
Get softer, brighter laundry, smoother shaving with less irritation, richer tea, indulgent baths in softer water, and better skin conditions against eczema and psoriasis.
4) Help the environment
Keep your appliances working well, use less water, and don’t need to clean limescale, which helps the environment.

Water hardness in the UK
Hard water is only created in areas where the pure rainwater comes into contact with porous ground. This means that there are some areas of the UK where water is much harder than others, though the majority of the country suffers to an extent.
- Over 200ppm of calcium and magnesium in your water is classed as hard water.

Hard water and eczema – A scientific correlation
A recent study by the University of Sheffield found that hard water makes skin conditions like eczema worse and can cause flare-ups. Also, hard water can make skin irritated, even in people with healthy skin. The study also said some people are more likely to get eczema, even if they don’t already have it.



